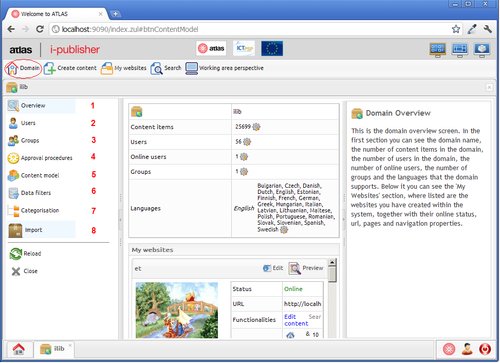
Domain functionalities
The picture above depicts the main areas in the domain entity:
- (1) Overview tab – shows the main stats for the domain:number of content items, number of users, groups, etc.
- (2), (3) , (4) , (6), (7) Users, groups, approval procedures, data filters and categorizations:these tabs follow the general pattern of the application and open corresponding lists. The details for these entities are described in the following sections.
- (5), (8) Content model and import – these two open specific editors, which will be described in separate sections.
The domain button(circled) allows you to go to the domain area from any other editor in the system.
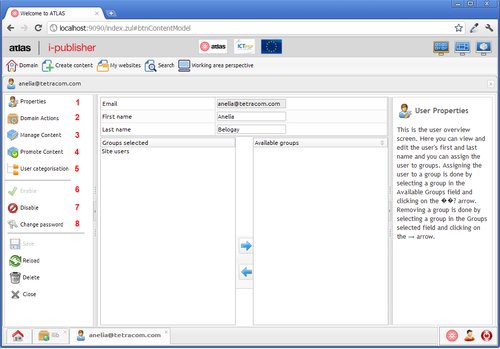
Users & Groups.
The users are the people who use i-Publisher. Besides the common properties(name,e-mail, etc.) each user has separate access rights, which allow them to use only specific parts of the i-Publisher interface. A group is a set of users, who have common access rights.
Points(1)-(4) are similar for both users and groups. Points (5)-(8) apply for user only.
-
Properties – defines general properties and relations between users and groups(which groups contain the given user and which users are in a given group).
-
Domain actions – defines the access rights for the various entities in the system(domain specific, site specific, system)
-
Manage content – defines the access rights for the content types in the system.
-
Promote content – defines the access rights for the approval chain of a content type.
Note: For more information about the access rights go to the hints area of each section in the system.
-
User categorization – specifies a user specific categorization tree.
-
Enable user – defines if the account is enabled or disabled.
-
Disable user - Disabled accounts can not log in the system.
-
Change password – opens a dialog, which allows to change the user's password.
Approval procedures.
These are build up of approval steps and allow content items to be in different states (for example “online” and “offline”). The bond between approval procedures and content items is created via the content type.
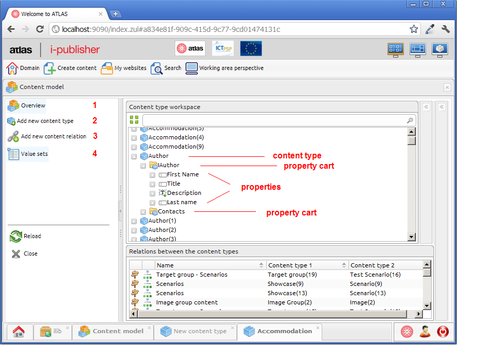
Content model.
The content model contains a group of content types. Each content type has one or more property carts. The latter represent a group of properties. To summarize – the content type is actually a container for properties. The content relations signify a link between two content types.
-
Overview – the overview tab shows the content model with the structure described above.
-
Add new content type – opens the content type details editor (depicted below).
-
Add new content relation – opens an editor, which allows the user to create a new content relation.
-
Values sets – example of value sets are:
-
Months – January, February, March, etc.
-
Yes/No value set
-
Countries
-
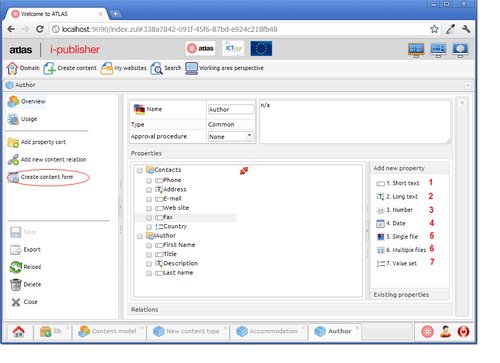
Content type details.
Above is the content type details editor. It allows the user to modify the content type by adding or removing properties. Also, here you define an approval procedure for the content items of the given type. There are seven types of content properties
-
Short text – shows a small text
-
Long text – shows a large text
-
Number – shows a number
-
Date – represents a date
-
Single file – a document or an image
-
Multiple file – one or more documents(or images)
-
Value set – a property, which value is one of the defined in the given values set.
How these properties are visualized in the content items is defined in the content form area (the circled tab in the editor). There you define maximum symbols of a text property, the format of date properties, how a file property is visualized(image, text, binary), whether the property is mandatory. Moreover, in this area you can specify which properties participate in the content items of the given type and how they are displayed.
Data filters.
The data filters define which content items will be shown in a list widget. They consist of expressions, which are combined together using boolean OR or AND.
Categorization.
The details of the categorization entity contains two tabs:
-
Properties – this is the place where the user builds their categorization trees. Each tree has a number of nodes, which are called categorization nodes. The latter are used to classify content items.
-
Automatic categorization – allows the user to build a categorization model for a given language based on the content items of a selected set of content types. Also, there are a group of categorization terms, which are assigned to the items based on their content.
Import.
Allows the user to import entities, which have been exported. In most details editors there is a button “Export”, which packages the entity and sends it to the Import area. Moreover, there are system entities (widgets, content types, whole sites), which can be imported.
ATLAS (Applied Technology for Language-Aided CMS) is a project funded by the European Commission under the CIP ICT Policy Support Programme.